Ever found yourself pondering the ease that Snowflake's date & time functions can bring to your data analysis? Imagine being able to quickly figure out the difference between dates, timestamps, or time between two events in Snowflake with just one single line of SQL. That's the magic of the Snowflake DATEDIFF function. Yet, while Snowflake DATEDIFF() might seem like easy to use, don't be fooled. This little function packs a punch! Get to know it well, and you'll be pulling out valuable insights from your data in no time.
In this article, we’ll cover everything you need to know about Snowflake DATEDIFF function. We’ll explain how it works, provide example usage for different cases, discuss when and why to use it, and share considerations and best practices.
Let's dive in!
What is Snowflake DATEDIFF() Function?
Snowflake DATEDIFF function is used to calculate the difference between two date, time, or timestamp values. It allows you to easily measure intervals like the number of days between two dates or the number of hours between two timestamps. It returns an integer representing the number of units between the two date/time expressions, which allows you to easily quantify time intervals like number of days between dates, hours between times, etc. Snowflake DATEDIFF supports date parts like year, month, week, day as well as time parts like hour, minute, second, millisecond down to the nanosecond.
It uses only the relevant parts of the date/time values to determine the difference. For example, if you specify “month” for a date value, it will only use the month and year, ignoring the day. This allows for precise flexible precision.
Also, remember that Snowflake allows the use of the minus sign (-) as an alternative method to subtract dates.
Note: Snowflake DATEDIFF() is used for date, time, or timestamp values, the minus sign is specifically for date values.

Want to take Chaos Genius for a spin?
It takes less than 5 minutes.

How does DATEDIFF() Work?
At its very core, the Snowflake DATEDIFF function operates based on a simple syntax:
DATEDIFF ( Date_time_value, Expression-1, Expression-2) Snowflake DATEDIFF function accepts three parameters:
1) date_or_time_part: The unit of time to calculate the difference in. Supported values are:
- DATE value: year, quarter, month, week, day
- TIME value: hour, minute, second, millisecond, microsecond, nanosecond.
2) date_or_time_expr1: The first date, time or timestamp expression to compare.
3) date_or_time_expr2: The second date, time or timestamp expression to compare.
With the help of these three parameters, Snowflake DATEDIFF function efficiently computes the difference and returns a value based on the specified unit.
Here is one simple example:
Select DATEDIFF(DAY, '2023-01-01', '2023-10-06');
/** Returns: 278 **/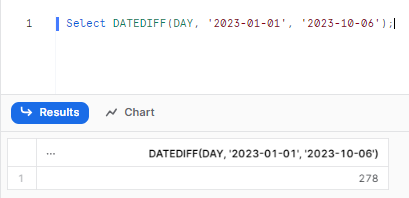
This counts the number of day boundaries crossed between January 1st and October 6th, returning 278 days. As you can see, the return value is an integer indicating the total number of unit boundaries. You can use this result in further calculations and analytics.
Practical Examples and Use Cases of Snowflake DATEDIFF
Now let's look at some more examples of using Snowflake DATEDIFF with different date and timeframes.
1) Calculate Difference in Years Using Snowflake DATEDIFF
This example calculates the difference in years between two timestamps:
SELECT DATEDIFF(YEAR, '2010-01-01 00:00:00'::TIMESTAMP, '2023-01-01 00:00:00'::TIMESTAMP) AS diff_years;Returns:
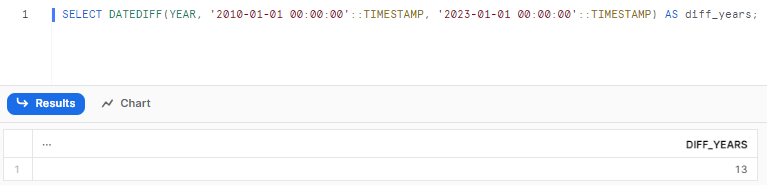
We can use this to find the number of years between any two timestamps. But, note that DATEDIFF(YEAR) accuracy decreases as the time period grows due to irregularities in the Gregorian calendar. It is best for shorter time spans.
2) Calculate Difference in Months Using Snowflake DATEDIFF
Finding months difference between two dates:
SELECT DATEDIFF(MONTH, '2023-01-01'::DATE, '2023-07-01'::DATE) AS diff_months;Returns:
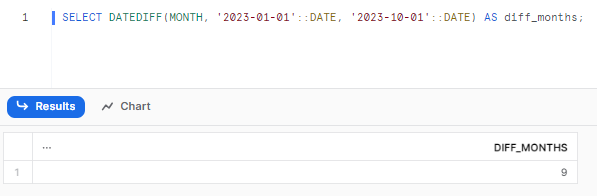
This calculates the number of months between the two dates. Useful for tracking monthly trends.
3) Calculate Difference in Hours Using Snowflake DATEDIFF
Get difference in hours between two timestamps:
SELECT DATEDIFF(HOUR, '2023-01-01 09:00'::TIMESTAMP, '2023-01-01 12:00'::TIMESTAMP) AS diff_hours;Returns:
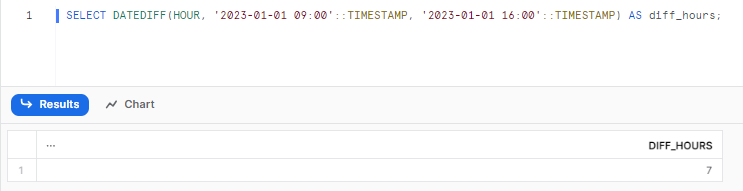
As you can see, this helps you find hourly intervals between timestamp values.
4) Practical Example of using Snowflake DATEDIFF function
Let's write one complete practical example of using the Snowflake DATEDIFF function. First, we will create a table, populate it with sample data, and use DATEDIFF() to calculate timespans between order and shipping timestamps. We can specify different date/time units to get the exact values we need.
-- Create database and schema
CREATE DATABASE order_data;
USE order_data;
CREATE SCHEMA sales;
-- Create orders table
CREATE TABLE sales.orders (
order_id INTEGER,
order_date TIMESTAMP,
shipped_date TIMESTAMP
);
-- Insert rows
INSERT INTO sales.orders
VALUES
(1, '2023-01-01 09:00:00'::TIMESTAMP, '2023-01-02 12:00:00'::TIMESTAMP),
(2, '2023-01-11 14:00:00'::TIMESTAMP, '2023-01-13 16:00:00'::TIMESTAMP),
(3, '2023-02-05 11:00:00'::TIMESTAMP, '2023-02-07 10:00:00'::TIMESTAMP);
-- Calculate shipping intervals
SELECT
order_id,
DATEDIFF(HOUR, order_date, shipped_date) AS shipment_hours,
DATEDIFF(DAY, order_date, shipped_date) AS shipment_days
FROM sales.orders;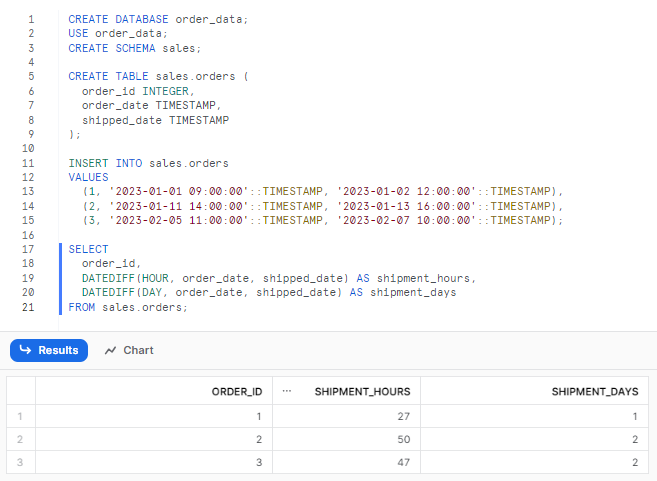
When to Use Snowflake DATEDIFF() Function?
Now that we've seen DATEDIFF() syntax and usage, let's look at where we can actually utilize this Snowflake DATEDIFF function and where it can help with date calculations and time span analysis.
Example 1—Calculating Days Until Product Expiry
Suppose you're a business managing your products. Keeping track of product expiration dates is crucial. Let's create a table for product expiry dates and add some sample products data:
CREATE TABLE product_expiry (
product_id INT,
expiry_date DATE
);
INSERT INTO product_expiry VALUES
(1, '2023-05-10'),
(2, '2023-06-15'),
(3, '2023-07-20'),
(4, '2023-08-25'),
(5, '2023-09-30'),
(6, '2023-10-05'),
(7, '2023-11-10'),
(8, '2023-12-15'),
(9, '2023-01-20'),
(10, '2023-02-25');To calculate the number of days until each product expires, and to display "Expired" if the product has already expired:
SELECT
product_id,
CASE
WHEN DATEDIFF(DAY, CURRENT_DATE, expiry_date) < 0 THEN 'EXPIRED'
ELSE CAST(DATEDIFF(DAY, CURRENT_DATE, expiry_date) AS STRING)
END AS days_until_expiry
FROM
product_expiry;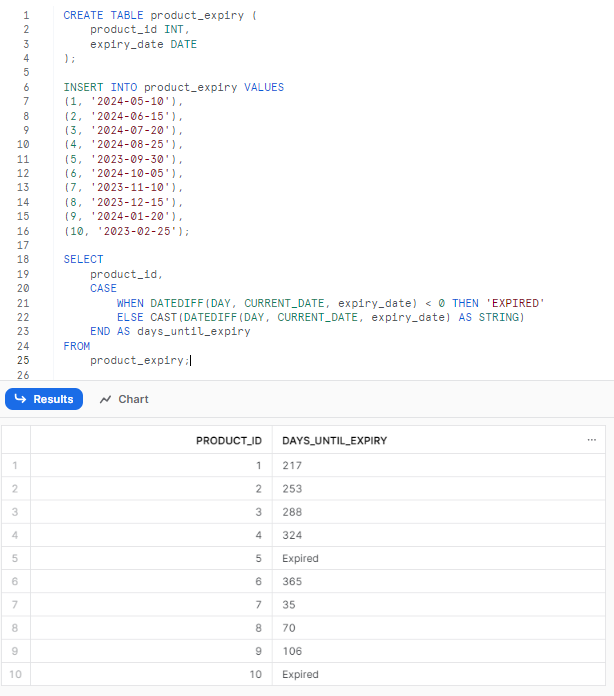
Example 2—Reporting and Analytics Over Time Periods Using Snowflake DATEDIFF
Let's try out one example to calculate the difference in days between the earliest and latest signup dates. First, let's create a table to track user sign-ups and insert some dummy data:
CREATE TABLE user_signups (
user_id INT,
signup_date DATE
);
INSERT INTO user_signups VALUES
(1, '2023-01-05'),
(2, '2023-01-15'),
(3, '2023-01-25'),
(4, '2023-02-05'),
(5, '2023-02-10'),
(6, '2023-02-20'),
(7, '2023-03-01'),
(8, '2023-03-10'),
(9, '2023-03-15'),
(10, '2023-03-25');Now, we can now use the Snowflake DATEDIFF function to calculate the growth between January and February:
SELECT
DATEDIFF(DAY, MIN(signup_date), MAX(signup_date)) AS days_difference
FROM
user_signups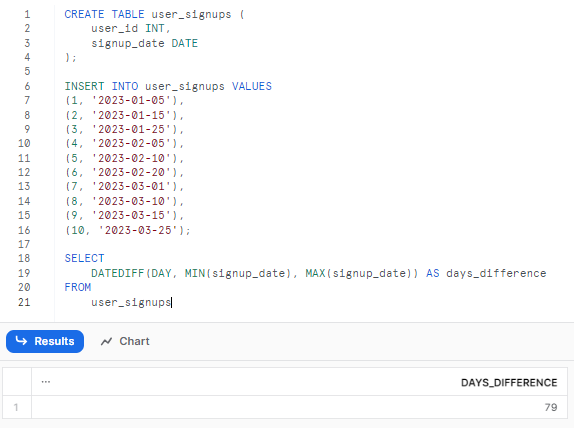
Example 2—Calculating Ages / Anniversaries / Years
Imagine you want to calculate the birthdays of users. First, we'd need to have a table with the data. But, for this example, we will create a table with some sample user birthdates.
CREATE TABLE user_birthdates (
user_id INT,
birthdate DATE
);
INSERT INTO user_birthdates VALUES
(1, '1990-05-10'),
(2, '1985-06-15'),
(3, '2000-07-20'),
(4, '1995-08-25'),
(5, '1980-09-30'),
(6, '1998-10-05'),
(7, '2002-11-10'),
(8, '1992-12-15'),
(9, '1988-01-20'),
(10, '1999-02-25');Now, lets use Snowflake DATEDIFF() function can help us determine the exact age of a user:
SELECT
user_id,
DATEDIFF(YEAR, birthdate, CURRENT_DATE) AS age
FROM
user_birthdates;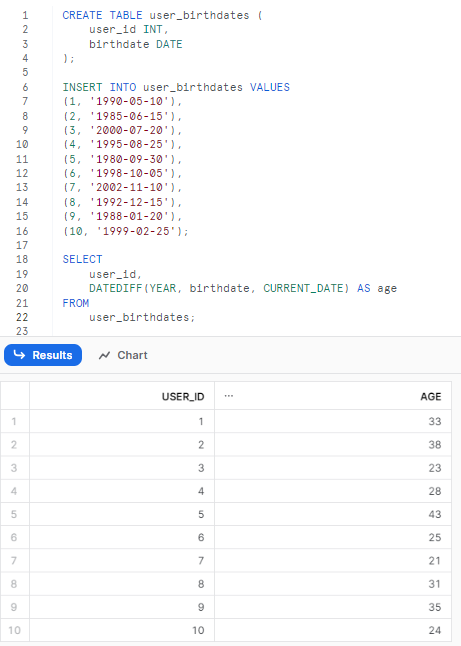
Example 3—Billing / Accounting Scenarios
Let's say we want to calculate subscription durations for billing purposes. To do so, first, let's create a table for user subscriptions:
CREATE TABLE user_subscriptions (
user_id INT,
start_date DATE,
end_date DATE
);
INSERT INTO user_subscriptions VALUES
(1, '2023-01-01', '2023-01-31'),
(2, '2023-01-15', '2023-02-14'),
(3, '2023-02-05', '2023-03-05'),
(4, '2023-02-20', '2023-03-20'),
(5, '2023-03-01', '2023-03-31'),
(6, '2023-03-10', '2023-04-09'),
(7, '2023-03-15', '2023-04-14'),
(8, '2023-03-20', '2023-04-19'),
(9, '2023-03-25', '2023-04-24'),
(10, '2023-03-30', '2023-04-29');To calculate the duration of each subscription:
SELECT
user_id,
DATEDIFF(DAY, start_date, end_date) AS subscription_duration
FROM
user_subscriptions;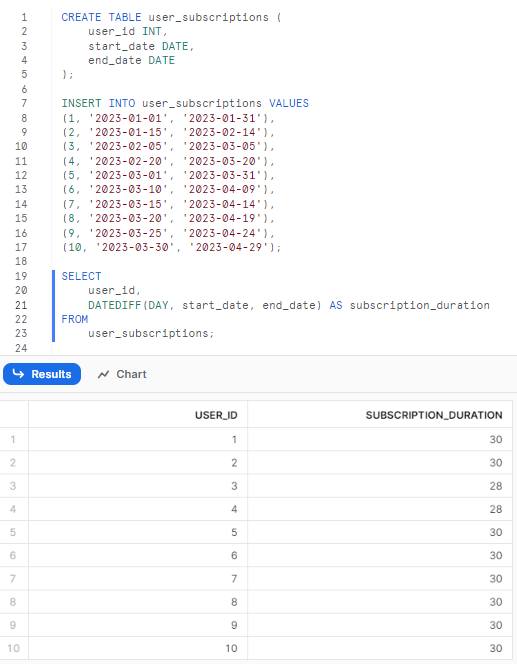
Example 5—Calculating Work Tenure of Employees
Let's say a company has several employees and wants to provide benefits based on their tenure. To manage this, first, we'll create a table for employees and add some sample data:
CREATE TABLE employee_start_dates (
employee_id INT,
start_date DATE
);
INSERT INTO employee_start_dates VALUES
(1, '2019-05-10'),
(2, '2018-06-15'),
(3, '2020-07-20'),
(4, '2017-08-25'),
(5, '2016-09-30'),
(6, '2019-10-05'),
(7, '2020-11-10'),
(8, '2018-12-15'),
(9, '2019-01-20'),
(10, '2020-02-25');To calculate the work tenure of each employee:
SELECT
employee_id,
DATEDIFF(YEAR, start_date, CURRENT_DATE) AS years_of_tenure
FROM
employee_start_dates;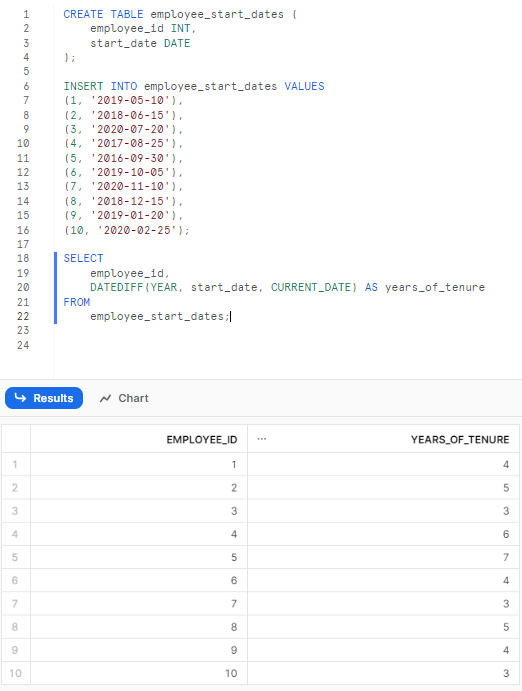
The use cases here are just a small sample—Snowflake DATEDIFF function can be used for virtually any date range calculations needed in data analytics.
Considerations and Limitations of Snowflake DATEDIFF()
There are some important factors to keep in mind to make sure you get accurate results, while using Snowflake DATEDIFF function.
1) Accuracy Decreases for Larger Units
The accuracy of the date calculation depends on the date part specified. Larger units like year and month are less precise than day or second. Let’s say for example, the difference between two dates may be closer to 1 month and 20 days, but specifying 'month' will return just 1. So larger units give a good estimate but shouldn't be relied on for precise measurements.
2) Daylight Saving Time Impacts
Daylight saving time transitions can impact the accuracy of Snowflake DATEDIFF function results. If the time range crosses a DST(Daylight Saving Time) change, the actual elapsed time won't match a simple calendar calculation.
So use caution interpreting Snowflake DATEDIFF results across DST transitions. It's safer to use smaller units to avoid this effect.
3) Leap Years Affect Year Calculations
In a leap year, February has 29 days instead of the usual 28. So Snowflake DATEDIFF() results can vary by +/- 1 day when calculating year differences across leap years.
To avoid surprises during analysis, it's better to use precise units like day rather than year estimates.
4) Date Part Selection Impacts Precision
As mentioned above, the date part impacts accuracy. Day and time units are precise, but year and month are estimates.
So carefully choose the date part needed for your analysis—don't use month if you need exact days for example.
5) Time Zones Need Consideration
Timestamps include time zones, which Snowflake DATEDIFF function will take into account. So results may vary across different time zones.
Standardize your date on UTC timestamps to avoid inconsistencies and daylight saving effects in regional time zones.
Limitations of Snowflake DATEDIFF
Here are some of the limitations of using Snowflake DATEDIFF function:
1) Limitations while Combining Multiple Units in Snowflake DATEDIFF
Snowflake DATEDIFF allows specifying only one date part, so you cannot directly combine units in the same query.
Workarounds exist using subqueries or variables, but they lack the native flexibility of other databases to return multiple units in one result.
2) Limitations with Negative Values in Snowflake DATEDIFF
Snowflake DATEDIFF doesn't work as intuitively with negative values. The negative result represents a reversed order of arguments rather than a reversed time flow.
So be very cautious when interpreting negative results—they indicate the first date is later than the second date rather than a time going backwards.
3) No Automatic Time Zone Conversion in Snowflake DATEDIFF
Snowflake does not automatically convert timestamps to a common time zone. So DATEDIFF() on timestamps in different zones may produce inconsistent results.
You need to explicitly convert timestamps to a consistent zone like UTC before using DATEDIFF() to avoid discrepancies.
4) Performance Impacts in Snowflake DATEDIFF
On extremely large datasets, making heavy use of Snowflake DATEDIFF function can have performance implications. It requires scanning LARGE volumes of data.
Try to isolate Snowflake DATEDIFF to where it is needed rather than using it directly on giant tables if query speed starts becoming problematic.
These limitations mean Snowflake DATEDIFF() requires some care and thought in practice, but don't prevent it from being highly useful. Just be very cautious while using it.
Snowflake DATEDIFF() — Performance and Cost Breakdown
Snowflake DATEDIFF is a simple built-in expression. It rarely causes slow performance by itself. Slow queries usually come from scanning too much data, poor pruning, or complex query shape. Performance and cost depend on how you use it and how much data you scan.
Performance
DATEDIFF()runs as a native SQL function and is inexpensive per row.- The dominant cost is data scanned. Scanning millions or billions of rows multiplies the work
DATEDIFF()must do. - Avoid calling
DATEDIFF()on a column inside a WHERE clause. For example, do this:
WHERE order_date >= CURRENT_DATE - 30Instead of this:
WHERE DATEDIFF(day, order_date, CURRENT_DATE) <= 30The latter applies a function to every row and can defeat micro-partition pruning.
- Use raw-column range predicates when possible. That preserves micro-partition pruning and reduces scanned bytes.
- If you repeatedly compute the same date difference, calculate it once and store it, or use a materialized view or computed column to avoid repeated per-query work.
- Warehouse size and concurrency matter. For short, heavy queries a larger warehouse can finish faster; for steady throughput use right-sized warehouses to control credit burn.
Cost (credits)
DATEDIFF()does not add a separate charge. Snowflake charges compute for the warehouse time used to run the query.- More scanned data and longer runtime equal higher credit consumption. Functions embedded in predicates can increase scanned bytes and runtime.
- Repeated inefficient queries, joins, or subqueries that force full-table scans drive up cost faster than the cost of any single SQL function.
Optimization Strategies:
- Use Snowsight Query Profile to monitor actual scanned bytes, execution steps, and bottlenecks.
- Query history views (for example
ACCOUNT_USAGE.QUERY_HISTORYor the appropriate INFORMATION_SCHEMA view) show runtime and scanned bytes. Use those to find high-cost queries. - Look for queries that scan many micro-partitions or produce large shuffle stages. Those are the cases where refactoring helps most.
TL;DR:
- Filter before you compute. Apply range filters on raw columns first.
- Avoid wrapping columns in functions in predicates.
- Cache or persist repeated computations that do not change often.
- Use clustering keys or partitioning strategy when queries repeatedly target narrow time windows.
- Measure: compare scanned bytes and runtime before and after changes. If scanned bytes drop, cost will follow.
- Auto-suspend idle warehouses and tune warehouse size to your workload pattern.
DATEDIFF() is not the usual bottleneck. Poor predicate design, unnecessary full scans, and bad data layout are. Fix those first and your queries will behave.
Additional Resources
For more on working with dates in Snowflake, check out these resources:
Save up to 30% on your Snowflake spend in a few minutes!


Conclusion
And that's a wrap! As you've delved into this article, it's clear to see just how powerful Snowflake DATEDIFF() function truly is. Acting like a time wizard, it lets you effortlessly leap between dates, timestamps, or time intervals with just a single line of SQL.
In this article we covered:
- How DATEDIFF() calculates date and time differences
- Syntax options and supported arguments
- Practical examples for different use cases
- When to effectively apply Snowflake DATEDIFF()
- Considerations and limitations of using Snowflake DATEDIFF
So, familiarizing yourself with Snowflake DATEDIFF function can genuinely revolutionize how you approach time data analysis. Hope this article has helped you understand the depth and utility of the Snowflake DATEDIFF function.
FAQs
What is the Snowflake DATEDIFF() function used for?
It calculates the difference between two date, time, or timestamp expressions based on the specified date or time part.
How does Snowflake DATEDIFF() differ from using the minus sign (-) in Snowflake?
Snowflake DATEDIFF() is used for date, time, or timestamp values, the minus sign is specifically for date values.
What are the possible units of time for the Snwoflake DATEDIFF() function?
It supports units like years, months, weeks, days, hours, minutes, seconds, milliseconds, microseconds, and nanoseconds.
How does the Snowflake DATEDIFF() function handle fractional seconds?
Fractional seconds are not rounded. For instance, milliseconds use the first three digits of the fractional seconds.
Can the output values of Snowflake DATEDIFF() be negative?
Yes, output values can be negative, indicating the second date is earlier than the first.
How does Snowflake DATEDIFF() handle date parts in its calculations?
The unit used to calculate the difference determines which parts of the DATE, TIME, or TIMESTAMP field are used, affecting the precision of the result.
Can Snowflake DATEDIFF() be used with both DATE and TIMESTAMP values?
Yes, Snowflake DATEDIFF() can be used with date, time, or timestamp values.
What is the difference between Snowflake DATEDIFF() and DATEADD()?
Snowflake DATEDIFF() calculates the difference between two dates, while DATEADD() adds an interval to a date.
Does Snowflake DATEDIFF() work with TIMESTAMP values?
Yes, Snowflake DATEDIFF() can take TIMESTAMP inputs and will calculate differences based on UTC datetimes.
What happens if I pass invalid dates to Snowflake DATEDIFF()?
Passing invalid date values will result in a SQL compilation error.
Can I use a column reference instead of a constant date?
Yes, Snowflake DATEDIFF() works with any date/timestamp column references just like constant date literals. This allows calculating differences between fields.
Can Snowflake DATEDIFF() be used to calculate the difference in nanoseconds between two timestamps?
Yes, using DATEDIFF(nanosecond, timestamp1, timestamp2) will give the difference in nanoseconds.









































